Cotton Losing Share to Man-Made Fibers
Contact:
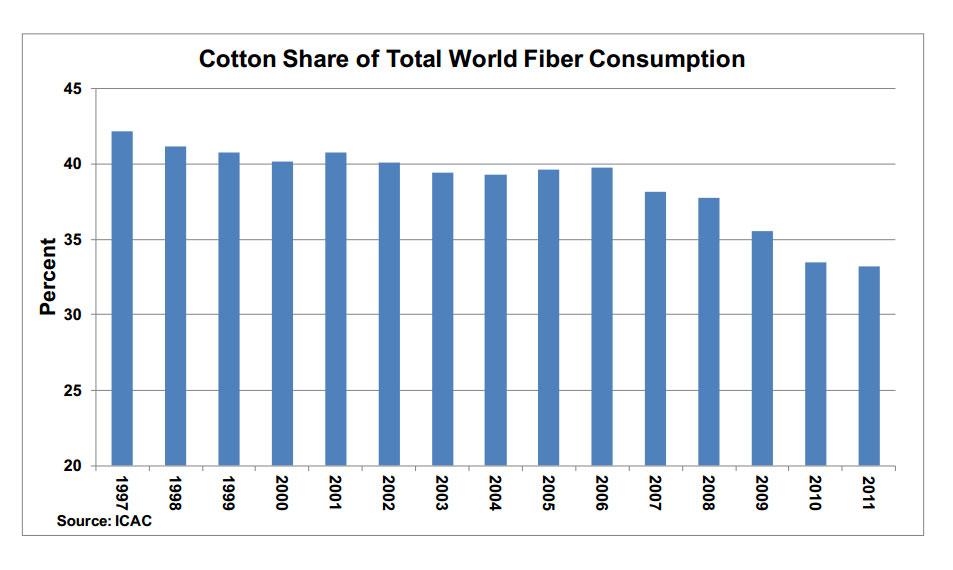
High cotton prices, especially relative to man-made fibers, have helped accelerate the decline in cotton’s share of global fiber consumption over the last several years. The International Cotton Advisory Committee (ICAC) reports that 2010 brought the largest single-year decline on record, in both absolute and percentage terms, when cotton prices reached record highs. Although cotton prices have fallen dramatically since then, they remain relatively high compared to manmade fibers
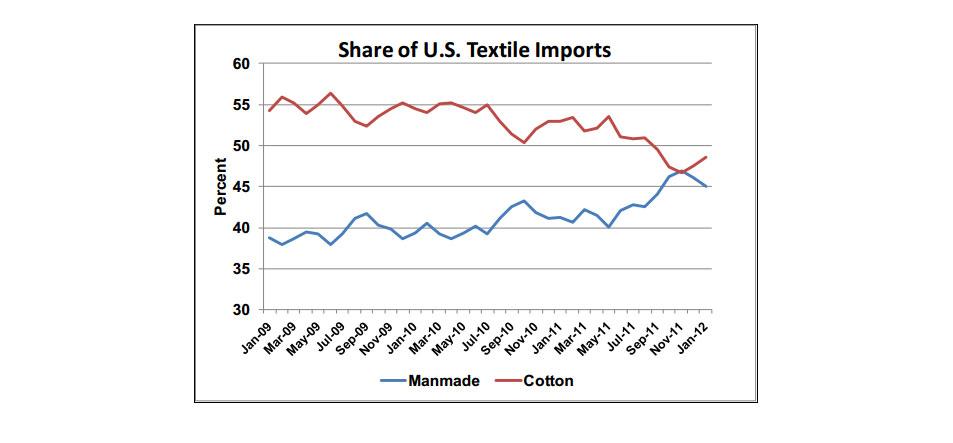
Declining global competitiveness is reflected in the U.S. textile market, where the share of cotton textile imports fell from 55 percent in July 2010 to 46 percent in November 2011. Imported textiles account for most of the U.S. retail market. Therefore, the drop in import share is a good indicator of the overall decline in the market situation, as higher-priced cotton passes through the supply chain.
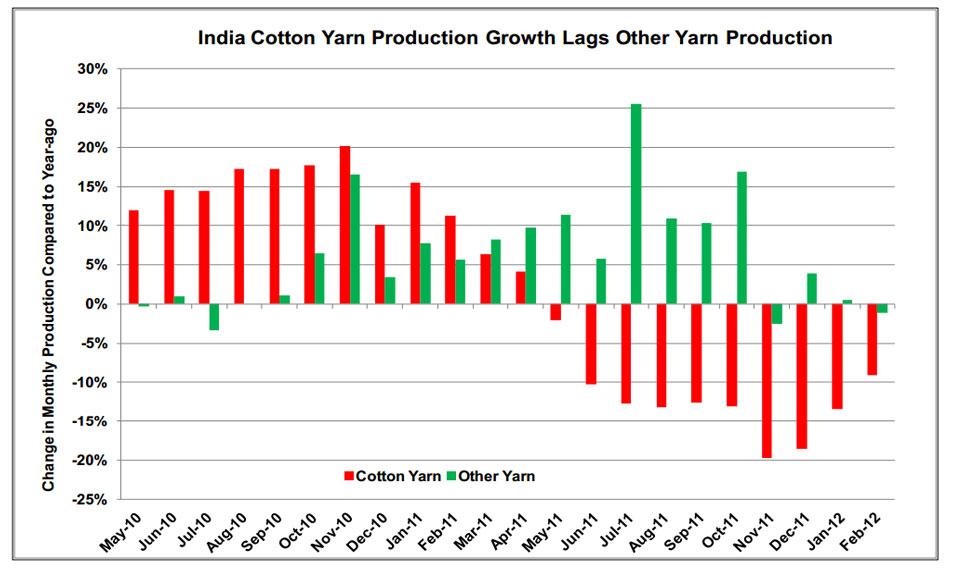
India provides another example of changing market dynamics caused by high cotton prices. Since April 2011, India’s production of cotton yarn has steadily declined, while production of other yarns has grown moderately. In contrast, from 2004 through 2010, India’s cotton yarn production had grown at twice the rate of other yarn production. Although India is a major textile exporter, most yarn production is used domestically. Therefore, India’s declining cotton yarn production, in absolute terms and relative to other yarn production, means cotton is being used less and holds a smaller share of a textile consumer market that it historically dominated.
The rapid rise and equally precipitous fall in cotton prices has caused disruptions across the supply chain disproportionate to the actual price changes. But perhaps more importantly, the perception or expectation of continued price volatility may have shifted the demand curve against cotton. Textile manufacturers and retailers, for example, have introduced man-made fibers into products that have traditionally been considered cotton products, and consumers have accepted this. It is possible that that even if the relative price of cotton returns to more historical levels, manufacturers may be reluctant to add more cotton back into these products.
